General surgeons at Bristol Health offer innovative surgical care, including robotic and laparoscopic surgeries, to improve your safety and speed up your recovery time.
Search Bristol Health
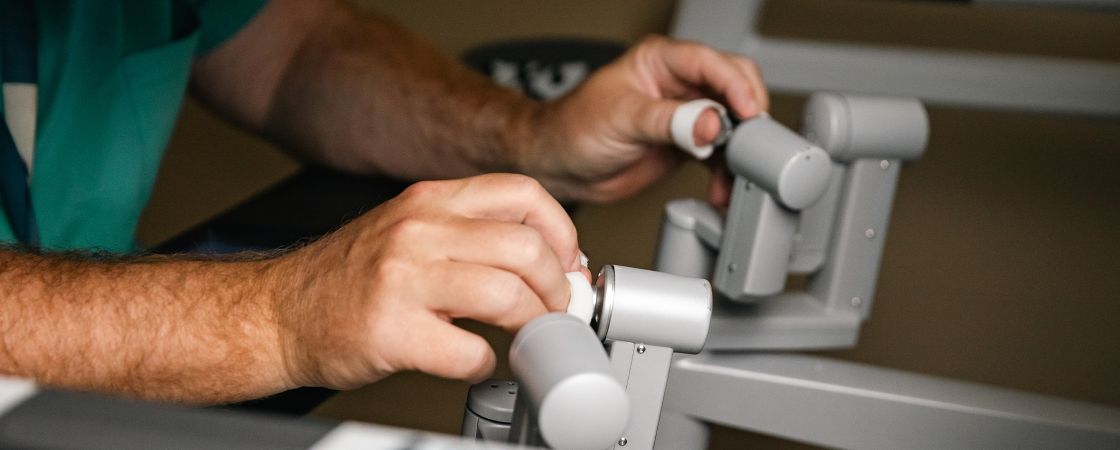

General Surgery
Programs & Resources
Advanced Surgical Treatment
We use the latest technologies and evidence-based care to improve patient outcomes and help you receive safe, effective surgical treatment. Our minimally invasive techniques reduce your risk for scarring, bleeding and infection while speeding up your recovery time.
General Surgery Procedures
General surgeons care for many conditions, from wounds to appendicitis, gastrointestinal cancers to digestive diseases. Below is a list of diagnostic and surgical procedures we commonly perform:
Meet Our Chief of Surgery
Chief of Surgery Jennifer N. McCallister, MD, FACS, is board-certified in general surgery and her range includes skin cancer surgery, hernia repairs, gallbladder surgery, breast surgery, colorectal surgery and advanced wound care.

The Center for Surgery and Endoscopy
Our state-of-the-art Center for Surgery and Endoscopy is designed with special sensitivity to our patients’ convenience and privacy needs. Beginning with arrival, patients will appreciate the convenience of the dedicated entrance and the canopied drop-off area.
Accompanying family members will find comfort in the large waiting area that has a coffee shop. Once brought into the clinical area, patients will enjoy the privacy and comfort of the bright and cheerful pre- and post-procedure rooms. To heighten comfort and diminish anxiety, rooms include a television for each patient. A dedicated pediatric recovery room allows loved ones the space and privacy needed to meet the unique comfort needs of children.
How Can We Help?
Can’t find what you’re looking for? Need a little more information? We’re happy to help!




